Navigating the Landscape: A Guide to Choosing the Right BI Tool for Your Business

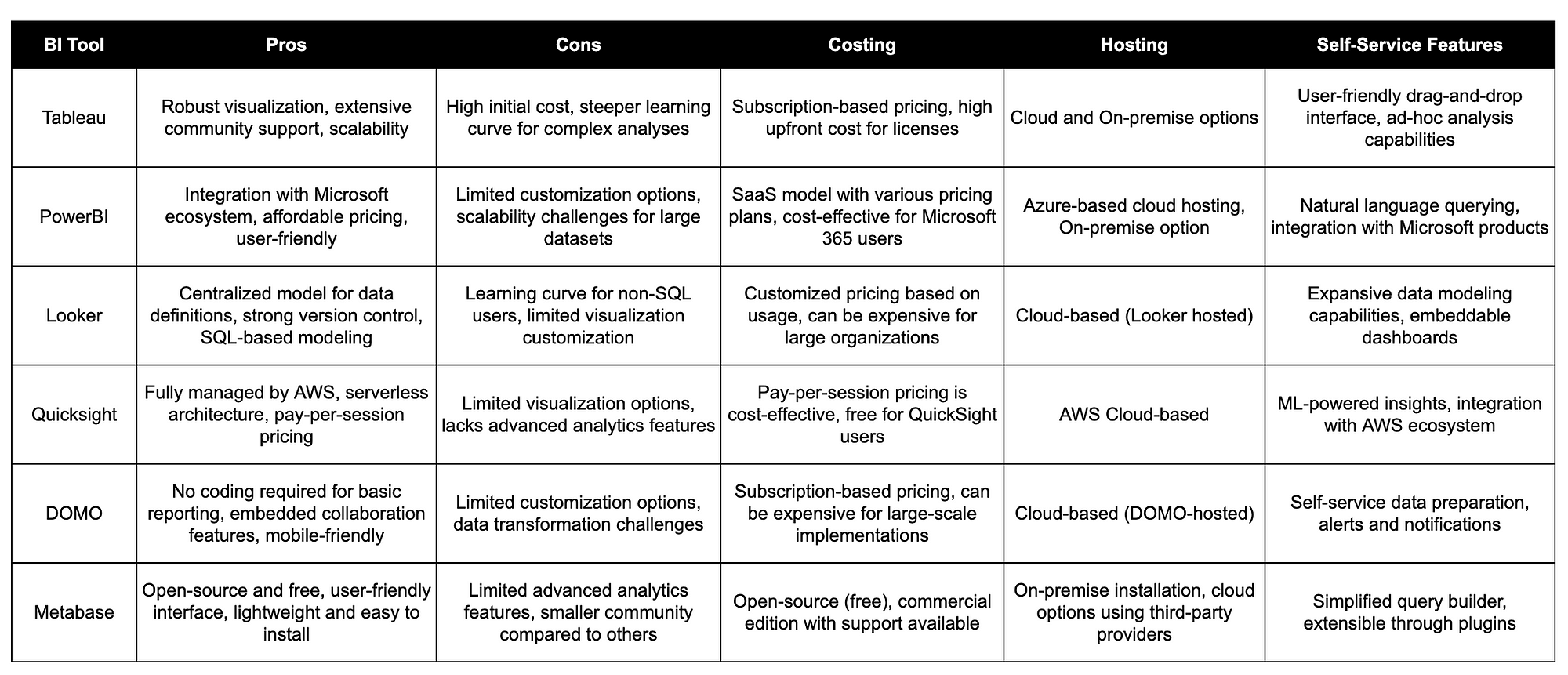
In the dynamic world of business intelligence, choosing the right tool can significantly impact your company’s analytical capabilities and decision-making processes. With myriad options available, aligning your BI tool choice with your specific use case and business requirements is essential. This article will guide you through the key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
- Define Your Objectives and Requirements
Before diving into the BI tool selection process, clearly define your business objectives and the specific requirements you seek in a BI solution. Consider factors such as data volume, user accessibility, integration capabilities, and the types of insights your organization needs.
2. Assess User-Friendliness and Accessibility
A good BI tool should be user-friendly, ensuring that all stakeholders, regardless of technical expertise, can extract meaningful insights. Assess the tool’s interface, ease of use, and the availability of user training resources. Additionally, check whether the tool supports mobile access for users who need insights on the go.
3. Evaluate Integration Capabilities
Ensure that the BI tool seamlessly integrates with your existing data infrastructure and other business applications. Compatibility with various data sources, databases, and third-party tools is crucial. Integration capabilities simplify the data flow and allow for a more cohesive analytics environment.
4. Scalability for Future Growth
Choose a BI tool that can grow with your business. Consider its scalability to accommodate an increasing volume of data, users, and analytical complexity. A tool that supports small-scale analytics and enterprise-wide BI ensures that your investment remains relevant as your business evolves.
5. Robust Data Security and Governance
Protecting your sensitive data is paramount. Look for BI tools that offer robust security features, including role-based access controls, data encryption, and compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, assess the tool’s governance capabilities to maintain data accuracy and consistency.
6. Understand the Cost Structure
BI tool costs can vary significantly based on factors such as licensing models, user seats, and additional features. Understand the tool’s pricing structure, and evaluate whether it aligns with your budget. Consider any potential hidden costs, such as implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
7. Analytical Capabilities and Flexibility
Different BI tools offer varying analytical capabilities. Evaluate whether the tool supports the types of analysis crucial for your business, such as ad-hoc reporting, predictive analytics, or machine learning integration. A flexible tool allows you to adapt to changing business requirements.
8. Seek User Feedback and References
User reviews and references can provide valuable insights into the real-world performance of a BI tool. Seek feedback from organizations with similar use cases, and inquire about their experiences with the tool’s implementation, support, and overall satisfaction.
References :
- Gartner Magic Quadrant: Industry insights and leaders.
- G2 and Capterra: Real user reviews for practical perspectives.
- Official Websites: For detailed features and current offerings.
Read More Such Content Here: LINK